- What is inflammation?
Inflammation is the response of the body’s immune system against external factors that can put your health in danger. When this system feels that is attacked by something that may harm your health, it activates some molecules that are called cytokines in order to neutralize or avoid any damage, so you can be safe.
- Why is it bad? What does it do?
Inflammation isn’t a bad thing since its purpose is to protect our body, but in some cases, when the duration of this response is extended for too long- I’m talking about years – it can cause harmful effects in your health. Especially, it can affect the brain by active transport of cytokines through this organ. Neuro-inflammation may occur if this process isn’t stopped by itself in early stages. This plays an important role in the development of mental diseases such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, schizophrenia, depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder (BD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), where elevated levels of inflammation have been found(1).
- What causes inflammation?
Inflammation can occur by different factors. Some of them could be:
Pathogens, injuries, chronic stress and diseases like dermatitis, cystitis or bronchitis to mention a few. Nutritional factors like overweight and poor diet quality can also trigger this process by increasing fat accumulation in our cells and damaging them (2). The exact mechanisms that are involved in these process still in research.
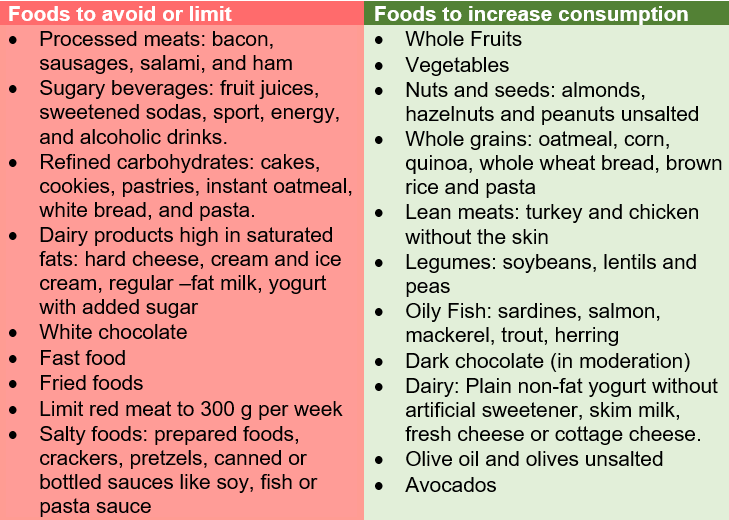
- What decreases inflammation?
Research has found that adhering to a healthy diet, like the Mediterranean diet, characterized by high intake of fruit, vegetables, whole grains, fish, lean meats and nuts, can decrease inflammation and protect you against depressive symptoms and anxiety (3,4). There is evidence that prebiotics, probiotics or synbiotics could also help you lowering inflammation. In addition, you should avoid eating pro-inflammatory foods which are foods that have been found to increase the risk of inflammation, and with it mental disorders. Some of these are refined carbohydrates, beverages with a lot of sugar added like soda, juice and sports drinks, processed meat and foods high in saturated fats (5).
- What are anti-inflammatory foods
Anti-inflammatory foods are the contrast of pro-inflammatory foods. These are foods that have been found to promote or induce low levels of inflammation in our body, which may protect us against neurological disorders. Briefly, these foods include fruits, vegetables, olive oil, fish and species like curcuma.
Here’s what YOU can do to minimize inflammation and improve your mental health.
This was co-authored by Josep Antoni Ramos-Quiroga, MD PhD psychiatrist and Head of Department of Psychiatry at Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron in Barcelona, Spain. He is also professor at Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona.
Reference
1. Mitchell RHB, Goldstein BI. Inflammation in children and adolescents with neuropsychiatric disorders: A systematic review. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry [Internet]. Elsevier Inc; 2014;53(3):274–96.
2. Ogłodek EA, Just MJ. The Association between Inflammatory Markers (iNOS, HO-1, IL-33, MIP-1β) and Depression with and without Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Pharmacol Reports [Internet]. 2018;70:1065–72.
3. Lassale C, Batty GD, Baghdadli A, Jacka F, Sánchez-Villegas A, Kivimäki M, et al. Healthy dietary indices and risk of depressive outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Mol Psychiatry [Internet]. Springer US; 2018;1.
4. Phillips CM, Shivappa N, Hébert JR, Perry IJ. Dietary inflammatory index and mental health: A cross-sectional analysis of the relationship with depressive symptoms, anxiety and well-being in adults. Clin Nutr. 2017;37.
5. Shivappa N, Bonaccio M, Hebert JR, Di Castelnuovo A, Costanzo S, Ruggiero E, et al. Association of proinflammatory diet with low-grade inflammation: results from the Moli-sani study. Nutrition. 2018;54:182–8.
